Back in the 1960’s, future depictions of the world were forecast with cars running on jet power, water or assorted powerplants – anything but petrol or diesel engines. This type of forward thinking – and dreaming – has led to some amazing advances over time, but to date there has been little impact or change to our reliance on petrol and diesel engines. Electric cars are the latest alternative energy to oppose the fossil fuel regime and with them are coming innovative new ways of thinking once more.
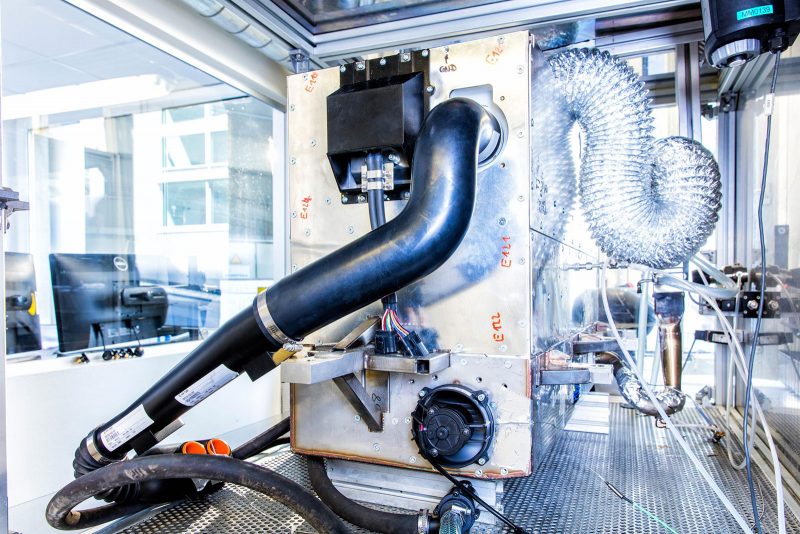
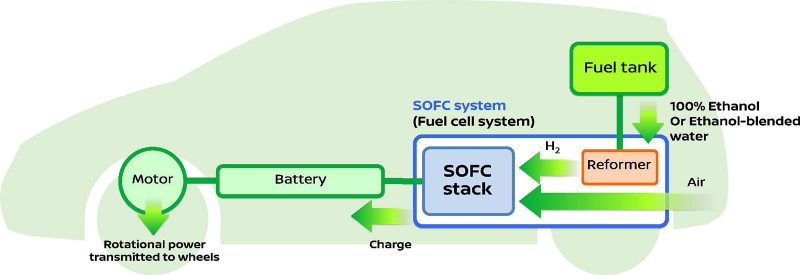
Today, Nissan has made public their research and development of a new Solid Oxide Fuel-Cell (SOFC) powered system that runs on bio-ethanol to produce electricity, powering an electric car. This marks the first time such a system has been used for an automotive purpose and features an e-Bio Fuel-Cell with an SOFC power generator. SOFC is a fuel cell using the reaction of multiple fuels, including ethanol and natural gas, with oxygen to produce electricity at a high efficiency.
The fundamental difference between Nissan’s research and a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle is what fuel the user has to put in. In fuel cells that store hydrogen, for example the Toyota Mirai and Hyundai ix35 FCV, cumbersome hydrogen tanks must be stored that can often negatively dictate the packaging of components within a vehicle. This can negatively impact boot space or seating as well as the implication of having to store a highly reactive gas too, despite the fact safety has been paramount in those vehicles. Nissan’s system differs in that hydrogen is produced in the car using a reformer. The advantage over storing hydrogen directly is two-fold. First, no new infrastructure would be required, which is often stated as the prime reason for slow interest in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. Second, packaging within the vehicle can be done more conventionally as the bio-ethanol can be considered much like petrol or diesel.
However, using this process does create one rather large problem – the production of CO2. Unlike a hydrogen fuel cell that has hydrogen stored and only produces water as a by-product, Nissan’s system will also produce CO2 emissions after the conversion of the fuel in the reformer. Nissan states that this may be indirectly overcome by the production of the bio-ethanol in the first place, as the crops grown to produce the fuel absorb CO2 as part of their photosynthesis. The company states that this is equal to the amount of CO2 produced from vehicles, although this would presumably depend on how many vehicles use the system.
Read on below to find out more from the official press release.
About e-Bio Fuel-Cell
The e-Bio Fuel Cell generates electricity through the SOFC (power generator) using bio-ethanol stored in the vehicle. The e-Bio Fuel-Cell uses hydrogen transformed from fuel via a reformer and atmospheric oxygen, with the subsequent electrochemical reaction producing electricity to power the vehicle – much like a conventional fuel cell that you might find in the Toyota Mirai or Hyundai ix35 FCV.
Unlike conventional systems, e-Bio Fuel-Cell features SOFC as its power source, affording greater power efficiency to give the vehicle cruising ranges similar to gasoline-powered cars (more than 600km). In addition, the e-Bio Fuel-Cell car’s distinct electric-drive features that includes silent drive, linear start-up and brisk acceleration – allow users to enjoy the advantages of a pure electric vehicle (EV).
Fuel-cell systems use chemicals that react with oxygen, generating power without release of harmful byproducts. Bio-ethanol fuels, including those sourced from sugarcane and corn, are widely available in countries in North and South America, and Asia. The e-Bio Fuel-Cell, using bio-ethanol, can offer eco-friendly transportation and create opportunities in regional energy production, while supporting existing infrastructure.
When power is generated in a fuel-cell system, CO2 is usually emitted. With the bio-ethanol system, CO2 emissions are neutralized from the growing process of sugarcane making up the bio-fuel, allowing it to have a “Carbon-Neutral Cycle,” with nearly no CO2 increase whatsoever.
The Future of e-Bio Fuel-Cell
In the future, the e-Bio Fuel-Cell will become even more user-friendly. Ethanol-blended water is easier and safer to handle than most other fuels. As this will remove limits on creating a totally new infrastructure, it has great potential for market growth.
Running costs will be remarkably low—on par with today’s EVs, ultimately benefitting the public as well as businesses, because the e-Bio Fuel-Cell is an ideal fit for wider customer needs because of the short refueling time and ample power supply that can support a range of services such as refrigerated delivery.
The Quest for a Zero-Emission Society
In pursuit of realizing a zero-emission and zero-fatality society for cars, Nissan continues to promote vehicle intelligence and electrification. Nissan’s brand promise of “Innovation That Excites” is delivered with “Nissan Intelligent Mobility”, which focuses on how cars are powered, driven and integrated into society through a more enjoyable driving experience.
The e-Bio Fuel-Cell will realize the concept of “Nissan Intelligent Power,” promoting greater efficiency and electrification of cars and the joys of driving, alongside battery EVs, such as the “Nissan Leaf”, “Nissan e-NV200,” and “e-Power,” which is equipped with an engine housing an exclusive large-capacity motor and power generator.
Nissan will continue to provide value to its customers by incorporating systems that enable the extraction of electric power from various fuels, while addressing the infrastructure issues tied to energy supply in every region of the world.
Source; Nissan